Get to Know Lupus
About Lupus
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to attack healthy tissue. This results in inflammation and damage to various parts of the body.
Get to Know Lupus
About Lupus
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to attack healthy tissue. This results in inflammation and damage to various parts of the body.
About Lupus Disease
Chronic Autoimmune Disease
It causes the immune system to attack healthy tissue resulting in inflammation, particularly of the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels and brain. It develops most commonly in women between the ages of 15-45, and occurs more often in African-American, Hispanics, Native Americans and Asians. Men can get lupus too. Lupus is not infectious or cancerous. People with lupus may have many different symptoms affecting various parts of the body. Some of the most common symptoms are extreme fatigue, painful or swollen joints (arthritis), unexplained fevers, skin rashes and kidney problems. Lupus is characterized by “flares” or periods of illness and remission.
Symptoms
There are a number of symptoms of lupus. Learning how to recognize these signs can help people maintain better health and reduce or ward off a flare. Currently, there is no cure for lupus but it can be managed effectively with drugs, and most people with lupus lead an active and healthy life.
Warning signs or symptoms of a flare can be increased
Extreme Fatigue
Rash
Fever
Headache
Hair Loss
Mouth Sores
Sun Sensitivity
Pain/Swelling in the Joints
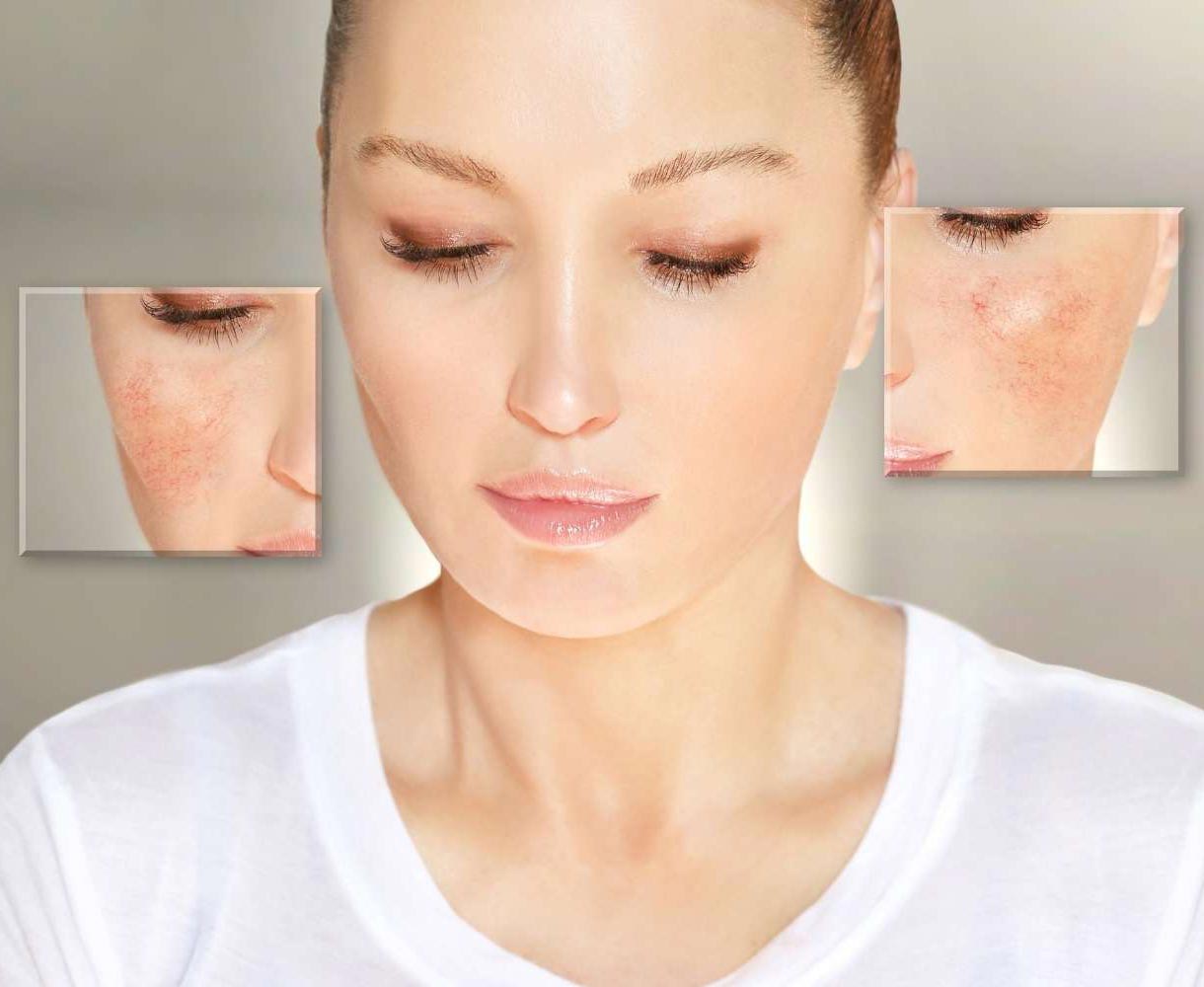
Types of Lupus
Anyone can get lupus, but it develops most commonly in women between the ages of 15-45. There are several types of lupus. Lupus can be difficult to diagnose because it mimics many other diseases. Often, symptoms develop so slowly that no pattern emerges, or they come and go. Lupus never affects two people in the same way. Early detection and treatment can usually lessen the progression and severity of this potentially debilitating disease. No single test can determine if a person has lupus. Some of the ways doctors diagnose lupus include a complete medical history, physical examination and laboratory tests.
1. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
It is the form of lupus most often referred to as lupus. The word systemic means the disease can affect many parts or systems of the body. Lupus nephritis is one of the most serious complications of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). A person with SLE may have mild or serious symptoms and usually affects a person between the ages of 15-45.
2. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
It only affects the skin. A red, raised rash may appear on the face, scalp or elsewhere. The raised areas may become thick and scaly. The rash may last for days or years and may recur. A small percentage of people with discoid lupus later develop SLE.
3. Drug-induced Lupus
It refers to a form of lupus caused by the use of certain medications. The symptoms go away when the drug is stopped.
FAQs about Lupus
Who gets lupus?
While lupus can occur at any age and in either sex, 90 percent of those living with lupus are female. Women are often diagnosed during the childbearing years, between the ages of 15 and 45. African Americans, Latinos, Asians and Native Americans have a higher risk for lupus. However, it can affect any ethnic group.
Although 10 percent of those with lupus are male, there is little information about why men get lupus. Some studies have found that after the age of 50, the percentage of women with lupus falls to 75 percent and the percentage of men with lupus increases to 25 percent.
Lupus can also affect children. It usually occurs at the age of 15 and older, however it can be diagnosed at any age. Children with lupus can have a large degree of kidney involvement. Severity of kidney involvement can alter the survival rate of people with lupus.
In rare cases, the newborn of a mom with lupus may have neonatal lupus. This condition can cause skin rashes, anemia or liver problems. Symptoms usually go away after a few months and don’t cause permanent damage. Some babies with neonatal lupus can be born with a serious heart defect. About 5 percent of the children born to individuals with lupus will develop the illness.
Is there a test for lupus?
There is no single test that can determine whether a person has lupus, but several laboratory tests may help the physician confirm a diagnosis or rule out other causes for symptoms. The most useful tests identify certain autoantibodies often present in the blood of people with lupus. For example, the antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is commonly used to look for autoantibodies that react against components of the nucleus, or “command center,” of the body’s cells.
What causes lupus?
While the cause is unknown, scientists suspect that individuals are genetically predisposed to lupus, and the disease remains quiet until a trigger sets the disease process in motion. Some outside environmental factor(s) create the right conditions for the disease to become active. The conditions that trigger lupus vary from person to person.
Only 10 percent of those with lupus will have a close relative (parent or sibling) who already has or may develop lupus. The chance increases to 50 percent if you have an identical twin with lupus. About 5 percent of the children born to individuals with lupus will develop the illness.
What do these terms mean?
Glossary of Terms
Why is lupus so difficult to diagnose?
There is no single diagnostic test for lupus. It can often take years for a diagnosis to be made because lupus may affect many systems within the body and many symptoms of lupus are similar to those of other diseases.
Systemic lupus is also difficult to diagnose because it is a disease that does not typically develop rapidly, but rather develops slowly and evolves over time. Symptoms or flares, which would lead to a specific diagnosis, may not appear all at once and can occur in different parts of the body over weeks, months or even years.
Making a correct diagnosis of lupus requires knowledge, awareness and good communication between you and your physician. An accurate medical history (for example, what symptoms you have had and for how long) is critical to the process. This information is combined with results of physical examinations and laboratory tests to lead to a diagnosis.
What is a flare?
A “flare” is a sudden change in disease activity. Lupus is unpredictable and patients often suffer flares, or active symptoms of the disease, followed by periods of remission (some doctors prefer to use the term “quiescence,” which means a quiet period). For those who have not been diagnosed with lupus, this continued recurrence of symptoms might be the first clue that lupus is the cause.
Lupus flares can be classified as mild, moderate or severe. An example of a milder flare might be the appearance of a rash. A very severe flare could cause fluid collection around the heart or even kidney failure.
What causes a flare is almost as unpredictable as when the flare will occur. There is no definitive way to predict when a flare will happen, how bad it will be, or how long it will last. When you have a lupus flare, you may have different symptoms than those you have had in the past.
You may find that your symptoms flare after you’ve been out in the sun and exposed to ultraviolet light, after a hard day at work or if you have not gotten enough rest. Stress, certain medications, infections, medication changes and even pregnancy can trigger flares in lupus patients.
Even if you take medicine for lupus, you may find that there are times when the symptoms become worse. If possible, learning to recognize when a flare is coming can help you take steps to cope with it.
Early signs of a flare in some individuals with lupus may include:
Increased fatigue
A new or higher fever
Increased pain
Development or worsening of a rash
Development of new symptoms
Swollen joints
The best way to manage lupus and avoid flares is to listen to your body, learn what your personal triggers and early warning signs are, and talk with your physician about them. If you think a flare is starting, it’s best to see your physician as soon as possible.
Where can I find more information online?
Lupus Research Institute
The Lupus Research Institute is the nation’s only nonprofit organization solely dedicated to novel research in lupus.
Could I Have Lupus?
This website, by the National Women’s Health Information Center, is part of a campaign designed to heighten awareness and create a sense of urgency about lupus.
The Lupus Initiative
The Lupus Initiative is committed to eliminating health disparities in lupus.
American College of Rheumatology, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
This site offers an extensive overview of the disease, it’s treatment and management, as well as helpful illustrations.
What type of specialist do I need?
Types of Specialist

Causes of Lupus
Scientists are making progress in understanding this complex disease whose cause is unknown.
A Complex Disease
Lupus is a complex disease whose cause is unknown. It is likely that a combination of genetic, environmental, and possibly hormonal factors work together to cause the disease. Research suggests that genetics plays an important role; however, no specific “lupus gene” has been identified. A healthy immune system produces antibodies, which are special proteins that help fight and destroy viruses, bacteria, and other foreign substances that invade the body. In lupus, the immune system produces antibodies against the body’s healthy cells and tissues. These antibodies, called autoantibodies, contribute to the inflammation of various parts of the body, causing swelling, redness, heat and pain.






